In Short…
- Common pricing approaches.
- Determine product price by using the Van Westendorp Price Sensitivity Meter.
- Implement the concept of strategic pricing to maximize the profitability.
Pricing is the most important lever for generating profit
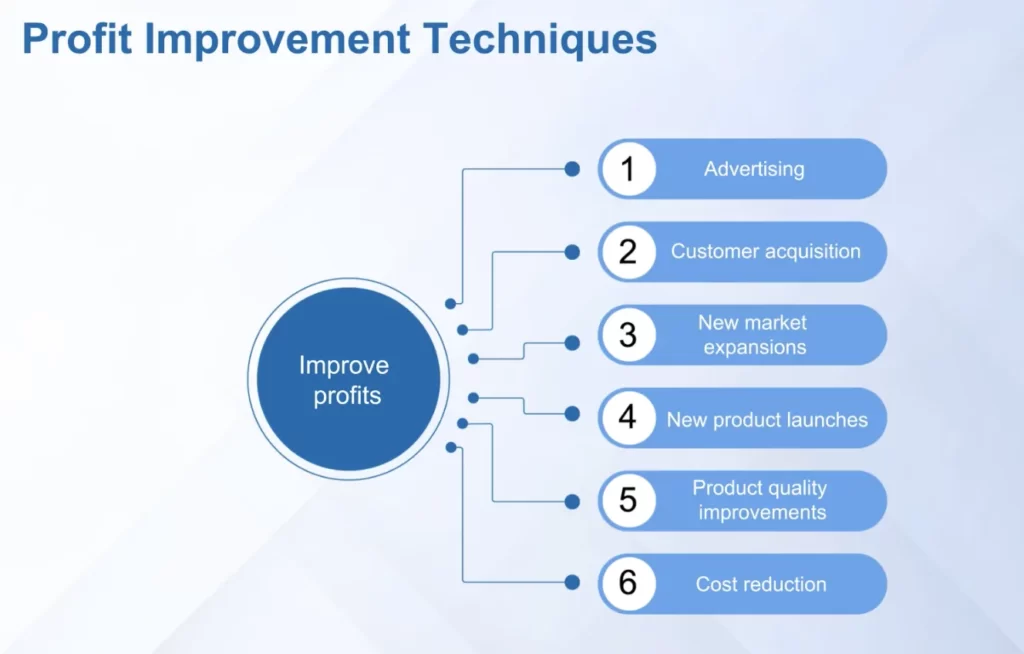
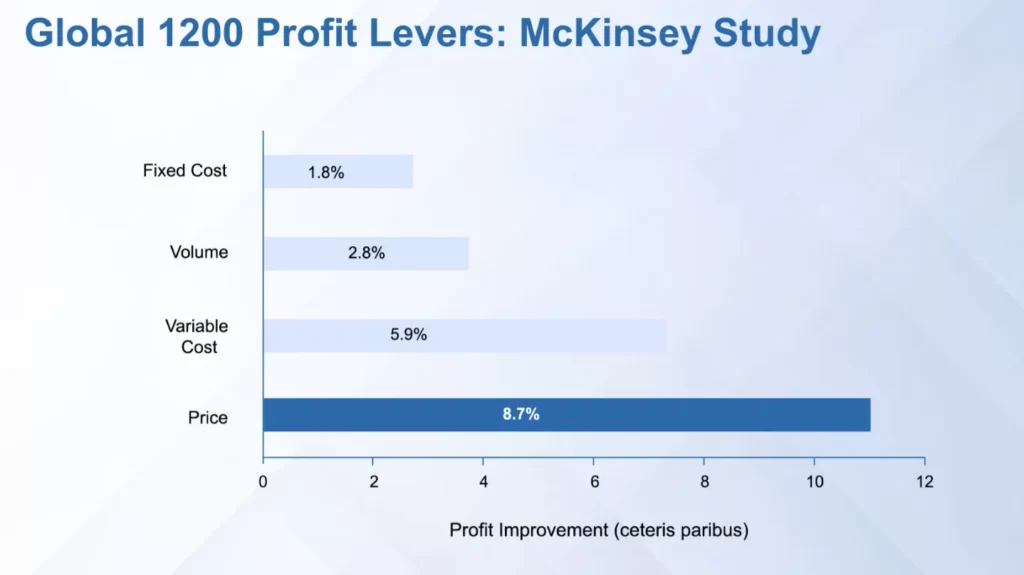
Pricing research is as important as pricing strategy.
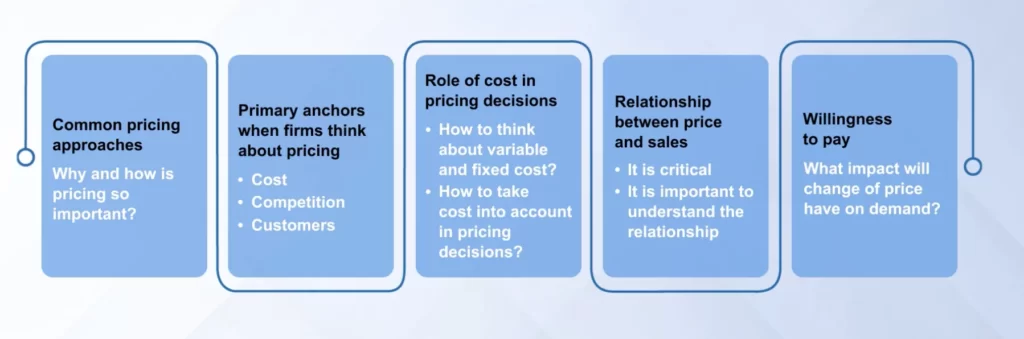
Pricing Approaches
Pricing can be at the industry level, product level, and transaction level.
Common pricing approaches:

But all these approaches are “anchored” on only three criteria:
- Cost
- Competitor
- Customer
Cost Plus pricing: Figure out the cost of manufacturing the product, then mark up (distribution cost, marketing cost, sales cost, expected profit, etc)
Hence competitor markups also need to be known.
But cost-plus pricing does not take customer value into account.
Competitive pricing: Price according to the competitor’s price.
It may lead to price wars, hence reduced profits.
Customer sales orientation price: How much is the consumer willing to pay?
Law of Demand
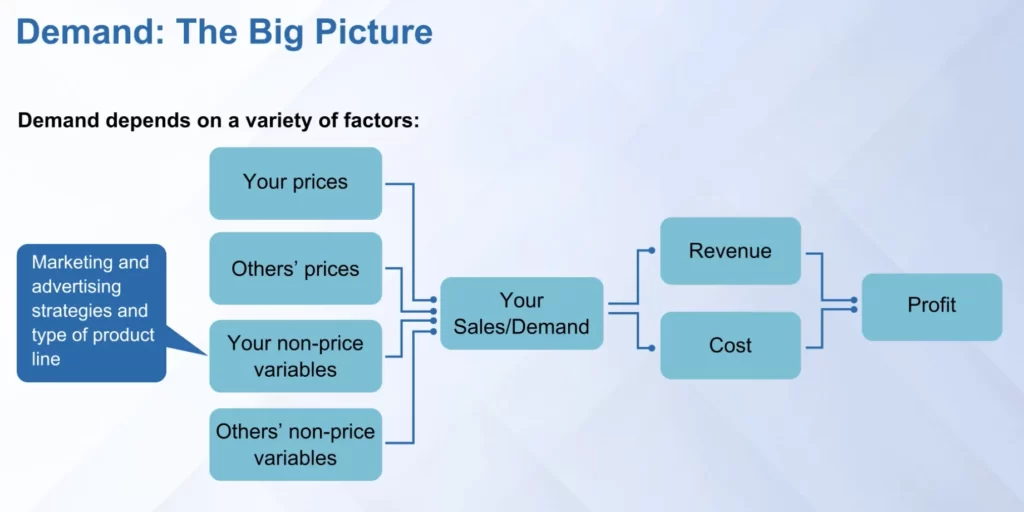
Pricing cannot be done in isolation

Price sensitivity can be found in 4 ways:
- Analytics of previous sales data
- Buyer Response surveys
- Conjoint studies
- Experiments in real-time
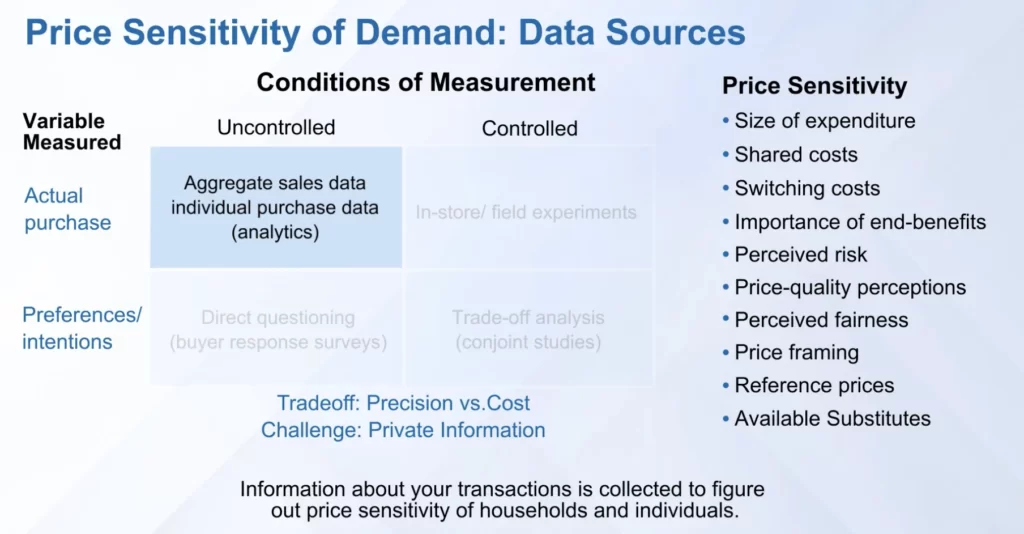
Price sensitivity is dependent on multiple factors:
- Size of expenditure
- Shared costs
- Switching costs, etc (refer the right side of the image above)
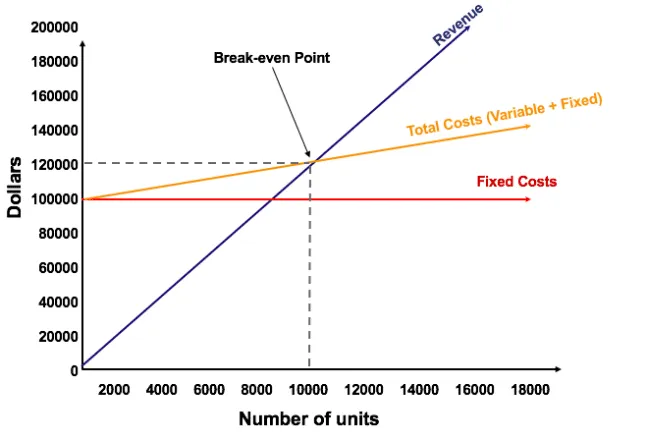
Role of Variable and Fixed Costs
Break-even analysis is important to price the product in such a way that it takes into account both fixed and variable costs at the unit level
Survey-Based Estimation Techniques
Methods to Determine Willingness to Pay

Delphi Method for Expert Judgement
In the early stage of product development, Expert Judgement is required to estimate:
- Expected production cost
- Expected Price
- Expected Revenue
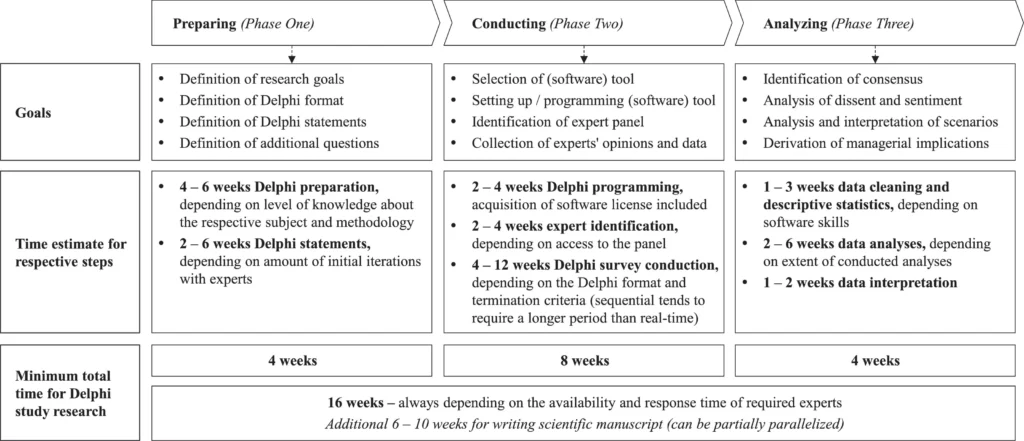
For expert judgment, the Delphi method is used. Delphi survey is for experts, not a generic population.
Delphi technique takes roughly 3-4 months to prepare the survey, conduct the survey and then analyze the survey
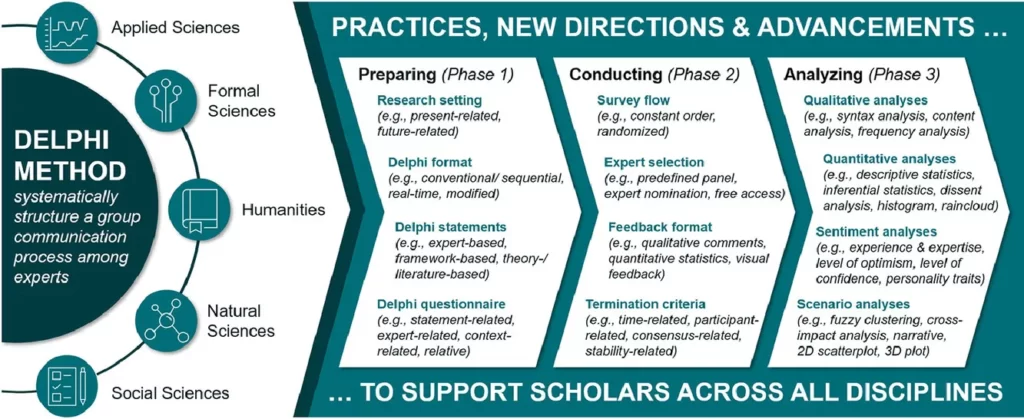
Another way to prepare, conduct and analyze the delphi method survey:
Purchase Intention Survey
How does the demand change when the price changes
We are interested in different price points at which customers are willing to pay to gauge demand
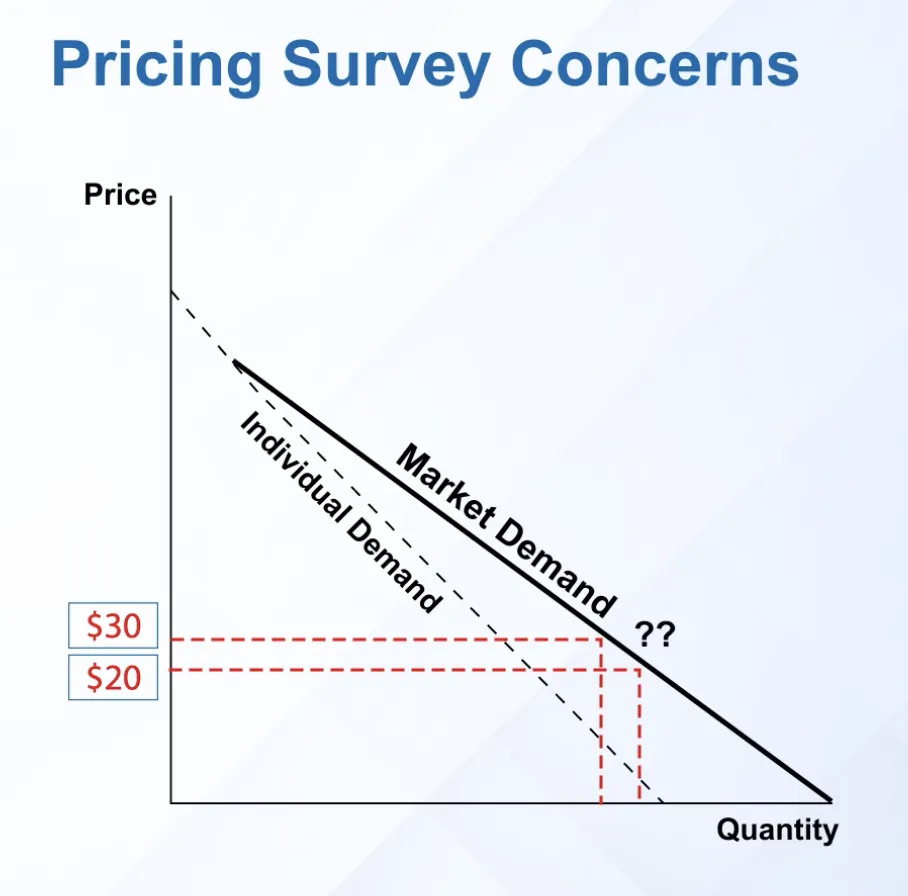
Although we are interested in understanding the price point, the survey should not lead with the price.
Instead of asking the same customer how much are they willing to pay ($10, $20 or $30), ask different customer segments.
Segment 1: If they are willing to buy at $10
Segment 2: If they are willing to buy at $20
Segment 3: If they are willing to buy at $30
This approach takes the mind of the customer away from just the price and makes them focus on whether the product adds value to them at a certain price.
Use a 7-point Likert Scale for all 3 segments pitching different prices.
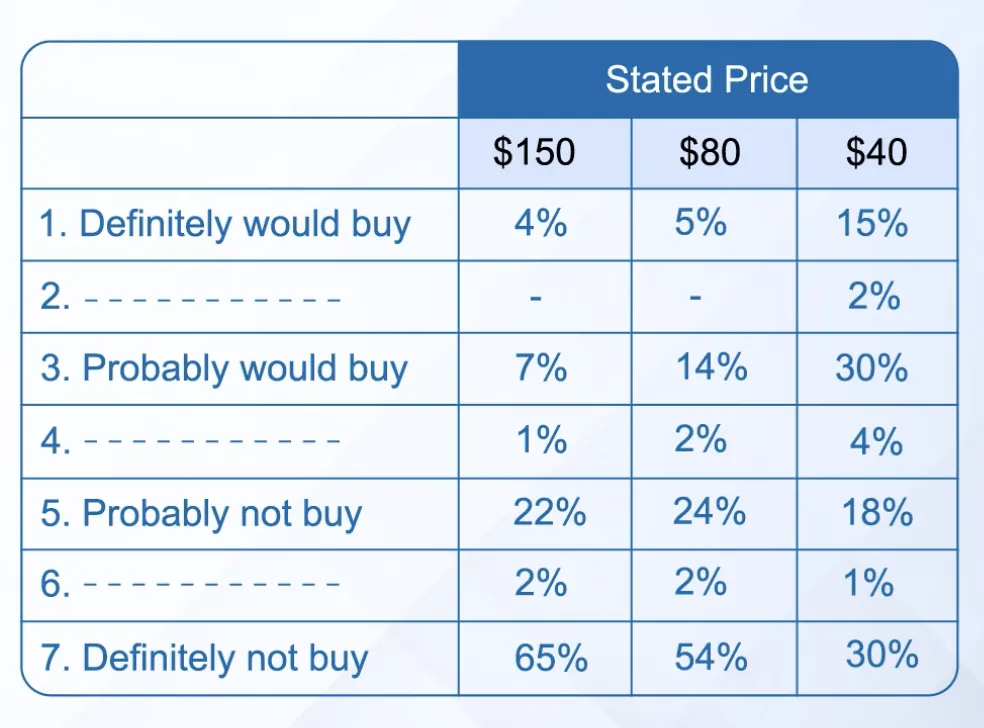
Select the percentage of people who are willing to buy versus the price point.
On the basis of the required profit, set the optimal price.

Van Westendorp Price Sensitivity Meter
Van Westendrop Price sensitivity survey takes into account two major risks of pricing:
- The product is priced too high compared to the paying ability of customers
- The product is priced too low, making it seem too good for this low price, hence creating doubt about the quality
For this 4 questions are asked in The Van Westendorp Model for Determining Optimal Price Point
- At what price would it be so low that you start to question this product’s quality? – Price-sensitive customer
- At what price do you think this product is starting to be a bargain? – Quality sensitive customer
- At what price does this product begin to seem expensive? – Price-sensitive customer
- At what price is this product too expensive? – Quality sensitive customer
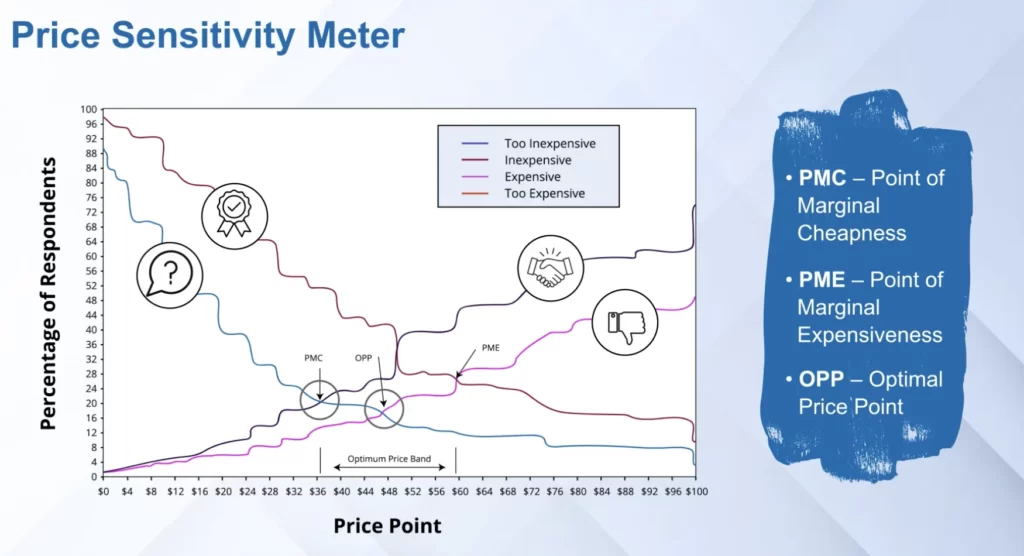
Based on the survey, a graph is plotted.
Responses to questions 1 and 3 are plotted (cumulative distribution) – intersection point is PMC (Point of Marginal Cheapness)
Responses to questions 2 and 4 are plotted (cumulative distribution)- intersection point is PME (Point of Marginal Expensiveness)
PMC and PME is the range of prices.
To figure out the OPP (Optimum Price Point), managerial judgment comes into the picture.
Note: These are notes from the ISB Executive Education – Product Management program for my personal consumption.
In case you are looking for a Product Management course, I would highly recommend joining this cohort-based course.
PS: You can connect with me for review or referral discount (link for referral discount)