In short…
- The importance of product positioning strategy in new product success.
- How to conduct a competitive analysis to know about the products within the same category.
- The different types of position strategies and how to manage a crisis that can impact the position of your product.
- Disruptive positioning strategies for market advantage.
- Managing a product’s position in the digital world.
- The challenges when introducing radical innovations to consumer markets.
Product Positioning and Its Importance
If a company is producing a high-quality product, but the market research says that consumers perceive the product as a medium-quality product.
This leads to an impact on the ‘consideration’ stage of the consumer purchase journey.
This is a ‘Positioning” problem because the position achieved is one of the most important factors in the planning and implementation of the marketing strategy or something has happened which has derailed the marketing strategy
Perfect positioning is when consumers collectively decide on a single point of view, a point of view the company wants the consumers to want to believe so that consumers would act and purchase the product.
e.g.: Apple iPhone is a premium product. Even after competitors have launched more expensive phones, consumers still believe iPhone to be a premium product compared to Samsung phones
How to Position a Product for Market Advantage
The traditional method of positioning
Perceptual Map is used for positioning. It helps understand the positions of different products in a market, on a set of factors driving customers’ purchases
Perceptual maps show Product benefits on key attributes (within the products category)
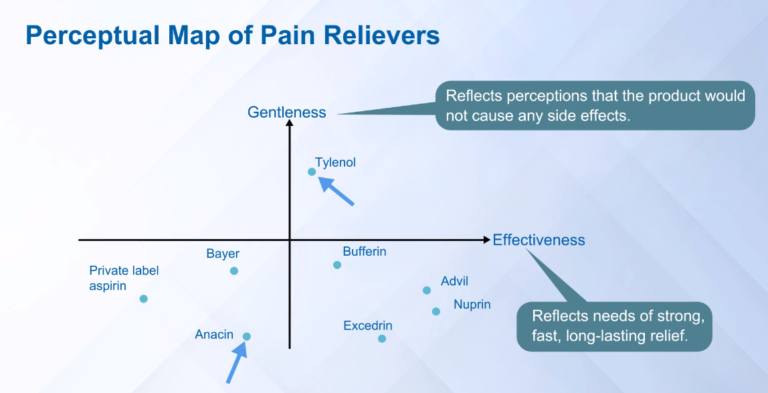
If price is an important factor, then a third axis of Price can be added. But this would lead to a 3D map which is difficult to understand.
Or there will be a series of three 2D maps. If price is an important factor, then a Value map is developed to showcase the value offered by each product in the category.
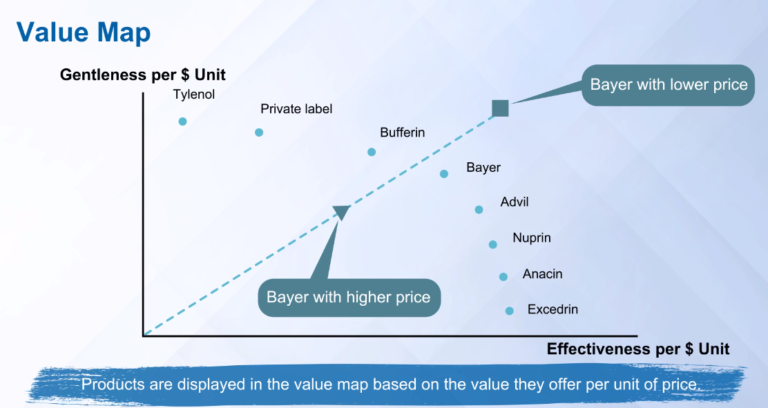
Hence significant innovation is required. Like in Marriot, for a loyal customer, even the room temperature is pre-set according to the customer’s last visit to the same hotel.
Product category has two major components:
- Category Structure: How competition is organized within the category
- Hierarchy: Tata Hotels (Ginger Hotel to Taj )
- Cluster: The cereal category is a cluster
- Category Identity:
- Category convention: What is expected from the category irrespective of the brand? This makes the differentiation of products difficult. (e.g.: Wifi in Hotels)
- Category Image: Salespersons are not trusted, but doctors are trusted even with personal information. Trust is the category image.
In traditional positioning, product differentiation becomes challenging because the focus is on key attributes (wifi in hotels, cab service by hotels). This is because consumers’ expectations keep on increasing. Over time expected value proposition of the category increases.
Hence significant disruptive innovation is required. Like in Marriot, for a loyal customer, even the room temperature is pre-set according to the customer’s last visit to the same hotel.
Understanding Disruptive Positioning
Instead of differentiating itself from other competitor products, differentiate the product from the entire category (e.g.: IKEA build-it-yourself model in the furniture segment)
It leads to positioning
Types of Disruptive Positioning Strategy:
- Reverse Positioning: Stripping away what is expected (when more features are better), stripping the unwanted features, and replacing them with high-end features focusing on the core needs
- iPhones didn’t have a customization option, unlike Android. It made switching to iPhone easier
- IKEA build-it-yourself model in the furniture segment. It defied the category connection. No salesperson helped the consumers. No delivery, financing, or assembly services. It focused on good design, low cost, gourmet food, and purchase experience.
- Breakaway Positioning: Creates a new product category altogether, thus breaking away from the current positioning of the product category
- Blackberry as a business phone
- Watch as a fashion category instead of a tool (showing time) category
- Alienware laptop: Gaming laptops
- Stealth positioning: Position the product in an entirely different category
- X-Box and PS were created as home entertainment hubs but were positioned as high-end game consoles.
- Insurance company masquerading as a consumer tech company: focus on the pain points of the insurance ecosystem like medicine delivery, healthy food joints listing, etc
Implementation of disruptive positioning
- Check the current status of the product: Analyze the category conventions and image, and check if consumers are satisfied with the current conventions
- Research alternatives: Can an alternate positioning be created with can address the dissatisfaction of the consumers?
- Company resources: Does the company have marketing competency, financial resources ad management conviction to execute a disruptive positioning strategy?
Planning a position for a new product
A perceptual map shows how consumers think about the brand, but not about the preference of the consumer
This is where Conjoint Analysis comes into the picture to take consumer preference into account.
Managing Position of Product in the Digital Age
Challenges in Introducing Radical Innovation to the Consumer Market
Radical vs. Disruptive Innovation: What They Mean for Organizations
In the case of radical innovation, 4 key aspects come into the picture for making the new product a success:
- What the product is? – Consumers don’t know what the product is
- How will consumers interact with it? – The company doesn’t know how consumers will interact with the product
- How well does the product work? – Consumers do not know how well the product works
- Will the consumers like the new product? – The company doesn’t know if the consumers will like the product
In the case of new products, sometimes the company launches an incomplete product and then uses market feedback to improve the product. (e.g.: FMCG has trial products that are given as samples with their best-selling products to gauge the interest of the consumers)
Explanations of the three disruptive positioning along with examples:
Reverse Positioning: Reverse positioning involves stripping away traditional features or elements that are typically associated with a product or service in order to create a simplified or stripped-down version that appeals to a different target audience. By removing certain aspects, the company aims to provide a more affordable, accessible, or user-friendly alternative.
Example: Southwest Airlines implemented reverse positioning in the airline industry. While other airlines focused on providing luxurious amenities and premium services, Southwest positioned itself as a no-frills, low-cost carrier. By eliminating features like assigned seating and in-flight meals, Southwest offered affordable air travel to a broader audience, targeting cost-conscious travelers who prioritize price and convenience over luxury.
Breakaway Positioning: Breakaway positioning involves challenging the conventions of an industry by introducing a new product or service that surpasses existing offerings in terms of performance, value, or innovation. The goal is to differentiate from competitors by offering a significant improvement or unique advantage that disrupts the market.
Example: Dyson is a prime example of breakaway positioning in the vacuum cleaner industry. Traditional vacuum cleaners relied on bags and filters for suction, but Dyson introduced bagless cyclonic technology that provided superior performance and eliminated the need for replacements. This innovation disrupted the market, capturing the attention of consumers who valued high-performance cleaning and the convenience of not having to purchase and replace disposable bags.
Stealth Positioning: Stealth positioning involves quietly entering a market with a disruptive product or service that gradually gains momentum and market share without drawing excessive attention from competitors or customers. It focuses on delivering a superior offering while strategically avoiding direct confrontation or competition with established players.
Example: Tesla employed stealth positioning when it entered the electric vehicle market. While established automakers focused on hybrid vehicles with limited electric capabilities, Tesla quietly developed and released the Tesla Roadster, an all-electric sports car with impressive range and performance. By targeting a niche market of luxury car enthusiasts initially, Tesla gradually gained recognition and built a strong brand presence. As the company expanded its product line and technology, it disrupted the automotive industry, becoming a major player in the electric vehicle market.
These disruptive positioning strategies demonstrate different approaches to challenging existing norms and capturing market share by offering something unique, different, or superior to traditional offerings
Note: These are notes from the ISB Executive Education – Product Management program for my personal consumption.
In case you are looking for a Product Management course, I would highly recommend joining this cohort-based course.
PS: You can connect with me for review or referral discount (link for referral discount)



